Industrial processes that require a fluid to be heated or cooled most likely use some form of tube heat exchanger. These devices are commonly used by producers because they are inexpensive and extremely reliable. The simplicity of their construction and the absence of moving parts makes them ideal for applications that require the removal or addition of heat. Read More…
Enerquip is your trusted shell and tube heat exchanger partner. Our in-house, thermal design engineers and ASME welders and fabricators can design and build custom engineered solutions for your company’s specific needs. Our experience and expertise have earned us a preferred supplier status with leading companies in the pharmaceutical, food and beverage, cannabis, personal care, chemical,...
Mason Manufacturing is a custom fabricator of shell and tube heat exchangers, ASME pressure vessels, columns, and tanks. Located in Decatur, Illinois, Mason has over 60 years of experience providing customers with custom fabricated vessels that conform to customer specifications, applicable codes, accepted industry standards and that are consistently shipped on time with competitive pricing. ...
At Tech Fab, we specialize in providing comprehensive solutions for heat exchangers, tailored to meet the diverse needs of our valued clientele. With decades of experience and expertise in the fabrication industry, we have established ourselves as a trusted leader, known for our unwavering commitment to quality, innovation, and customer satisfaction. Our product offerings encompass a wide range...
Since 1983, we have been providing quality heat transfer products for a wide variety of applications. We repair, rebuild or manufacture heat exchangers, tube heat exchangers, shell heat exchangers and double-wall heat exchangers. Electronics, hospitals and housing industries depend on us.

Since 1930 we have been a leader in providing control solutions and process equipment at McRae Engineering. Our product offerings include heat exchangers, agitators, boilers, vacuum pumps, process heaters, dampers, centrifugal blowers, and more. We also provide various repair services for our customers. Our experienced engineers will work with you to ensure all your specifications are met. Our...

At Lone Star Thermal Engineering, we specialize in providing comprehensive solutions for heat exchangers tailored to meet the diverse needs of our valued clientele. With our expertise in the field of thermal engineering, we have established ourselves as a trusted leader known for our commitment to quality, innovation, and customer satisfaction. Our product portfolio encompasses a wide range of...

More Tube Heat Exchanger Manufacturers
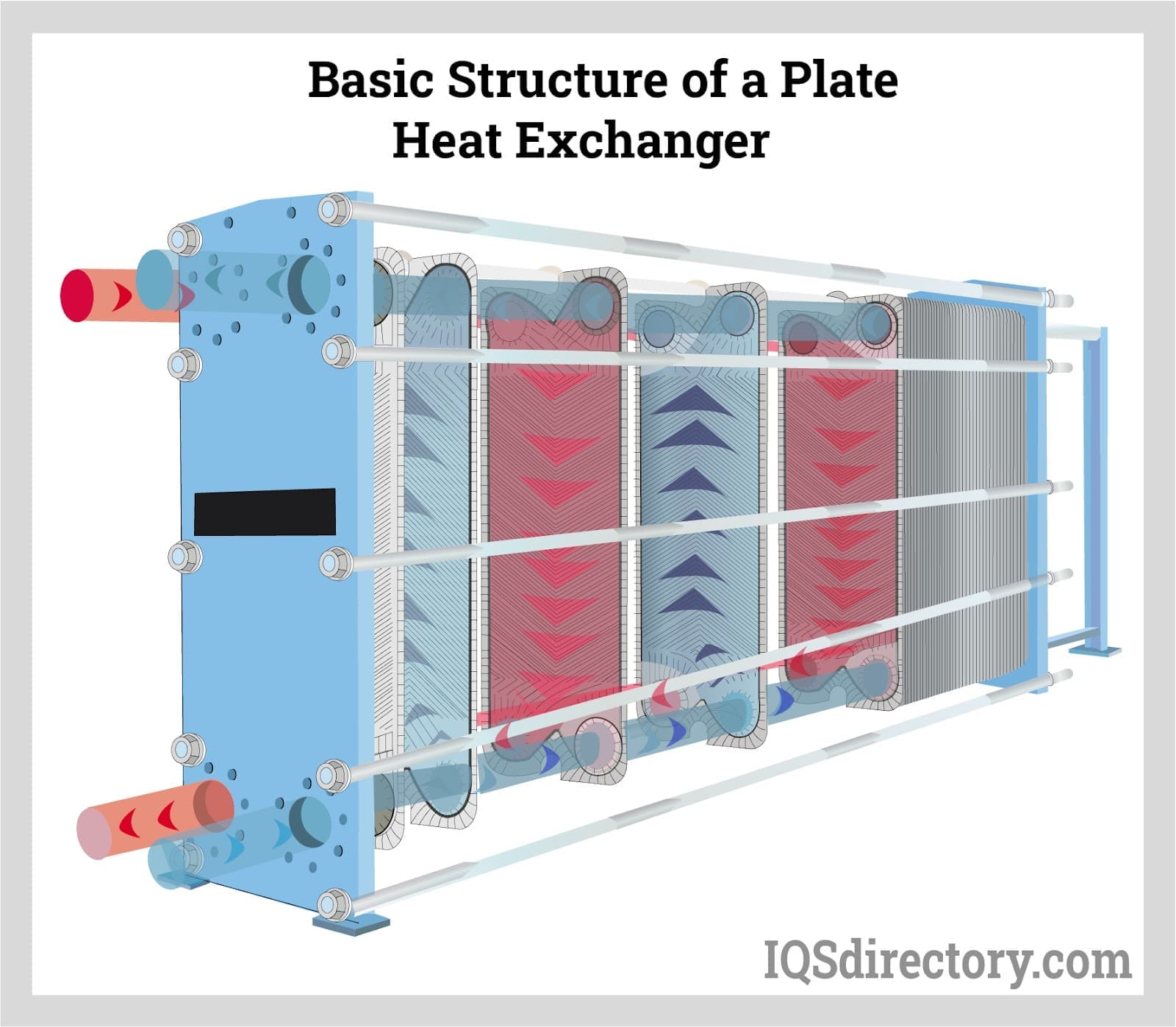
Tube heat exchangers are highly adaptable and can be used for a wide variety of applications. This particular characteristic makes them useable for the heating or cooling of liquids and gases. They are typically used with equipment that generates heat during operation and assist in controlling and removing the heat. This aspect of their operation prevents the rise in heat and keeps the manufacturing process safe.
What is a Tube Heat Exchanger?
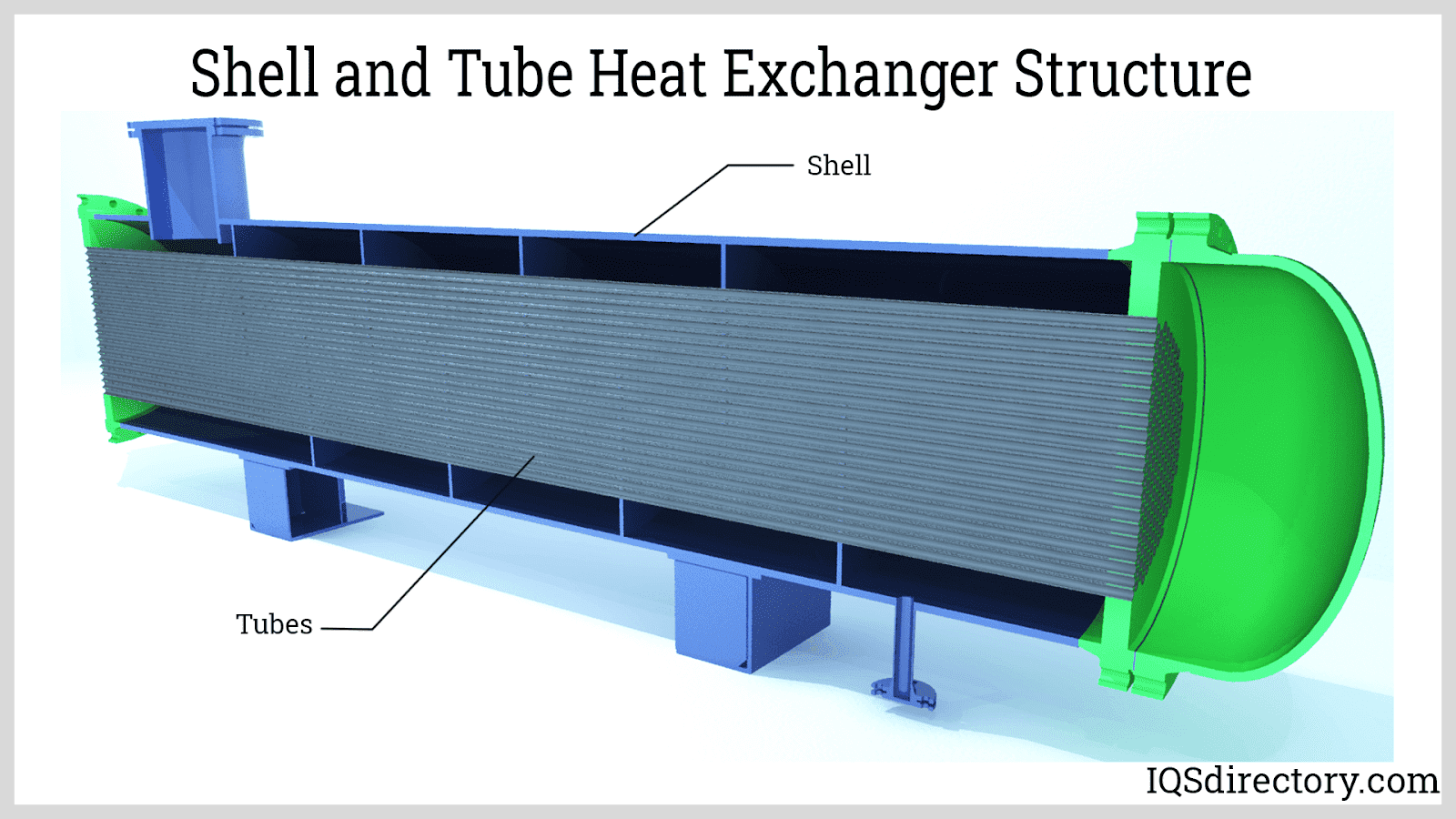
When describing a heat exchanger, it is commonly referred to as a shell and tube heat exchanger since both elements of the device work together to cool and heat liquids and gases. The process includes the flow of fluids inside the tubes of the exchanger and the shell. The exchange process happens when a cold fluid enters the shell through the inlet nozzle and exits as a hot fluid.
The transfer of heat in a shell and tube heat exchanger is decided by the exposed surface area and the number of thermally conductive tubes. The variations in the type of flow can be parallel or cross. The number of tubes vary according to the design of the heat exchanger with number of tubes being odd or even depending on the type of tube passes.
How a Tube Heat Exchanger Works
A shell and tube heat exchanger has two basic components, which are the shell and channel, or tubes. The shell side consists of a shell, cover, flange, nozzles, and support. The tube side is made up of the channel, cover, flange, nozzles, tube sheet, and tube bundles. The tubes can be arranged in a variety of geometric configurations, which include triangular, rotate triangular, square, and rotated square.
To create more turbulence and increase the velocity of the flow, a baffle is installed in the shell section. Since it enhances flow time, it creates the better possibility of heat exchange, which makes the heat exchanger more efficient. A further function of the baffle is to serve as support for the tubes to prevent damage and suppress vibrations.
Methods of Classifying Tube Heat Exchangers
Tube heat exchangers are classified by various aspects of the process, the type of flow, and the type of fluids. The first consideration is the operation of the heat exchanger and whether it is recuperative, regenerative, or direct contact. In the recuperative type of exchanger, fluids do not mix. In the regenerative type, the same surface is exposed to hot and cold fluids. Direct contact exchangers have liquids mix and interact.
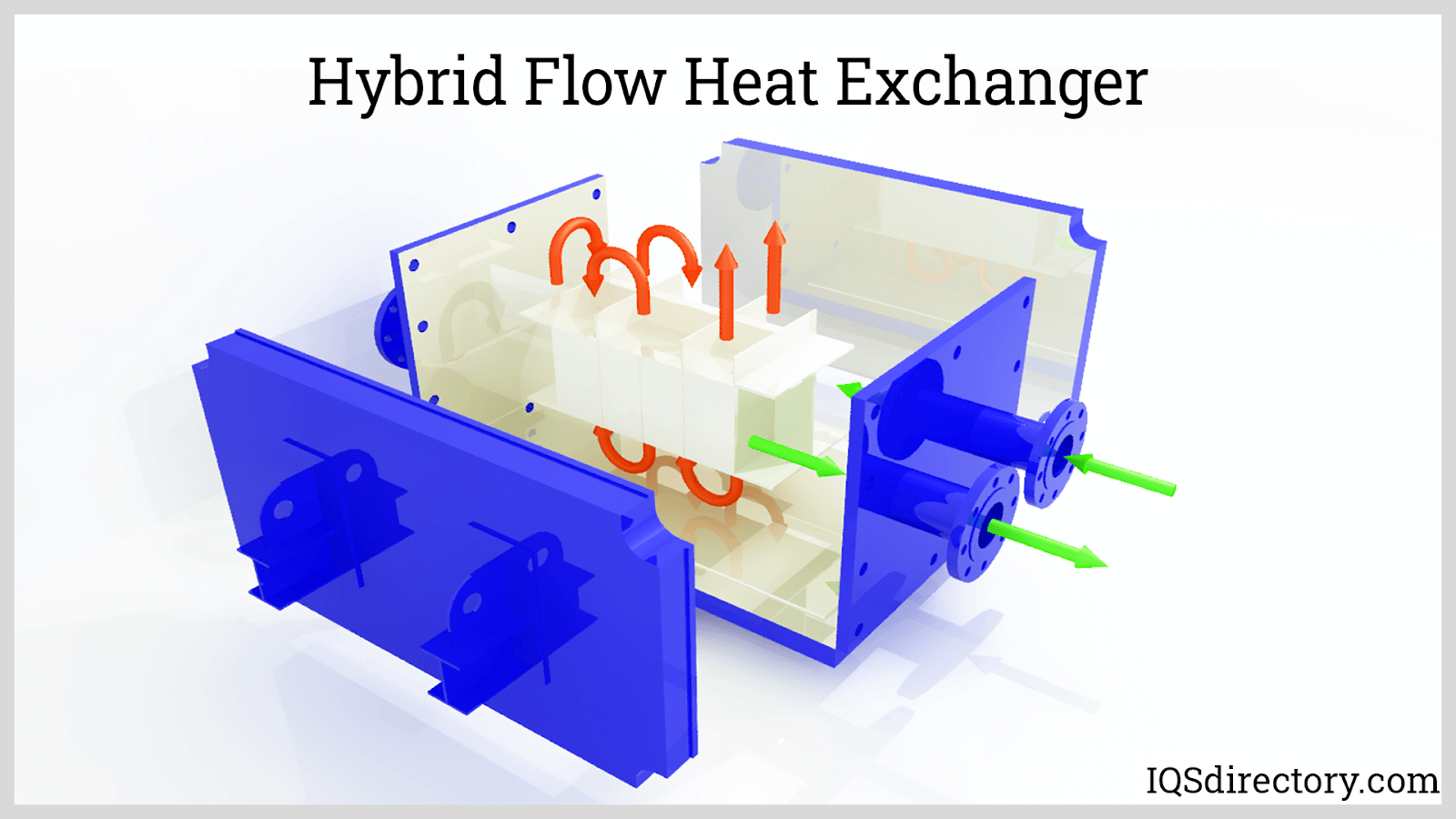
The next method of classifying tube heat exchangers is the type of flow, which can be co-current, counter current, or cross flow. In the co-current type, hot and cold fluids flow in the same direction and are unidirectional. The reverse of co-current is counter current where fluids flow in opposite directions. The third type of flow is when fluids flow across one another at right angles, which is cross current.
There are any number of functions for heat exchangers that include ones for chillers, heaters, evaporators, coolers, boilers, and condensers. The type of process for a heat exchanger depends on its purpose in the manufacturing process where cooling of equipment may be necessary for some processes while dissipation of heat may be necessary for another process.
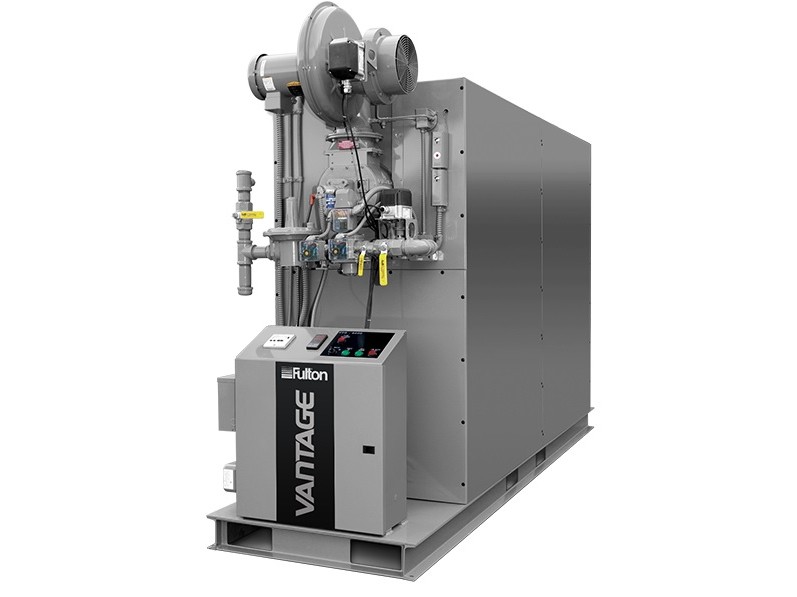






 Boilers
Boilers Chillers
Chillers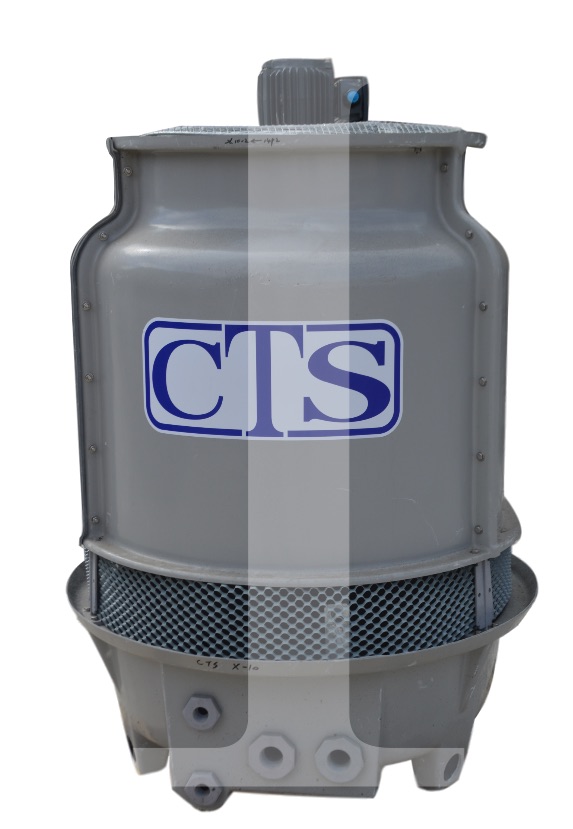 Cooling Towers
Cooling Towers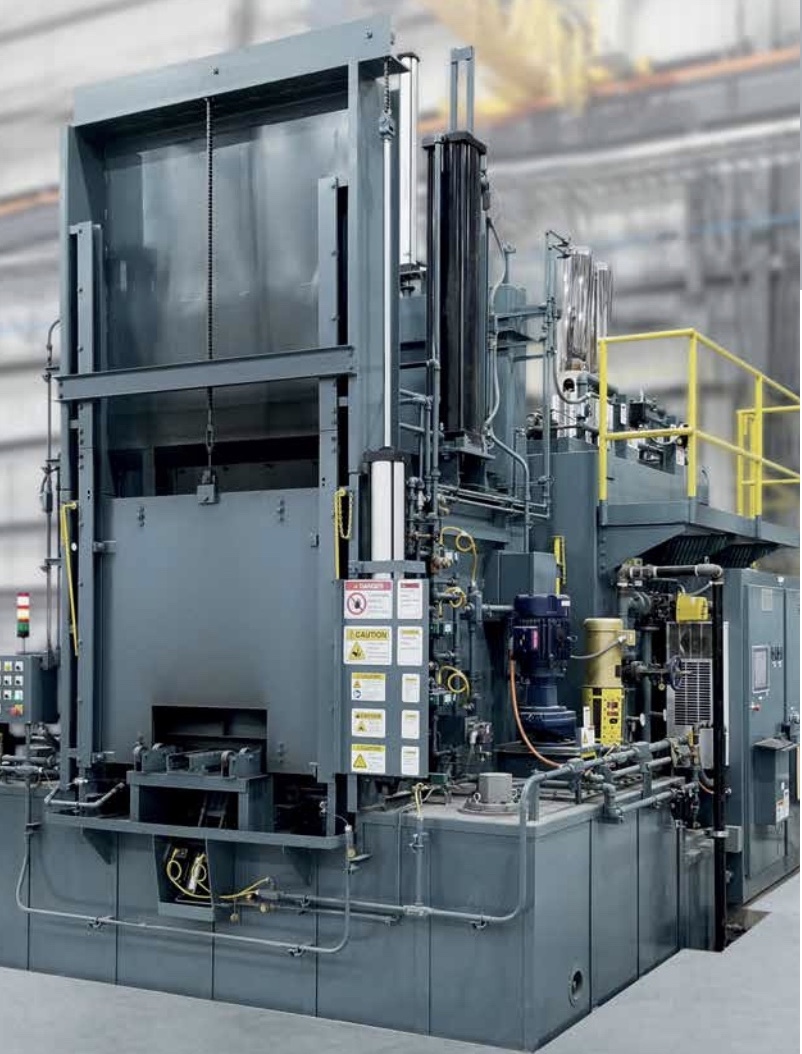 Furnaces
Furnaces Heat Exchangers
Heat Exchangers Heat Transfer Equipment
Heat Transfer Equipment Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services